That’s One Smart Hospital! Taiwan Medical Centers Deploy Life-Saving Innovations With NVIDIA System-Builder Partners
Leading healthcare organizations across the globe are using agentic AI, robotics and digital twins of medical environments to enhance surgical precision, boost workflow efficiency, improve medical diagnoses and more.
Physical AI and humanoid robots in hospitals have the potential to automate routine tasks, assist with patient care and address workforce shortages.
This is especially crucial in places where challenges to optimal healthcare services are paramount. Such challenges include hospital overcrowding, an aging population, rising healthcare costs and a shortage of medical professionals, all of which are affecting Taiwan, as well as many other regions and countries.
At the COMPUTEX trade show in Taipei, NVIDIA today showcased how leading Taiwan medical centers are collaborating with top system builders to integrate smart hospital technologies and other AI-powered healthcare solutions that can help reduce these issues and save millions of lives.
Cathay General Hospital, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CGMH), National Taiwan University Hospital (NTUH) and Taichung Veterans General Hospital (TCVGH) are among the top centers in the region pioneering healthcare AI innovation.
Deployed in collaboration with leading system builders such as Advantech, Onyx, Foxconn and YUAN, these solutions tap into NVIDIA’s agentic AI and robotics technologies, including the NVIDIA Holoscan and IGX platforms, NVIDIA Jetson for embedded computing and NVIDIA Omniverse for simulating virtual worlds with OpenUSD.
CGMH Boosts AI-Powered Medical Imaging
With an average of 8.2 million outpatient visits and 2.4 million hospitalizations a year, CGMH estimates that a third of the Taiwanese population has sought treatment at its vast network of hospitals in Taipei and seven other cities.
The organization is pioneering smart hospital innovation by enhancing surgical precision and workflow efficiency through advanced, AI-powered colonoscopy workflow solutions, developed in collaboration with Advantech and based on the NVIDIA Holoscan platform, which includes the Holoscan SDK and the Holoscan Sensor Bridge running on NVIDIA IGX.
NVIDIA Holoscan is a real-time sensor processing platform for edge AI compute, while NVIDIA IGX offers enterprise-ready, industrial edge AI purpose-built for medical environments.
Using these platforms, CGMH is accelerating AI integration in its colonoscopy diagnostics procedures. Deployed in gastrointestinal consultation rooms, the AI-powered tool collects colonoscopy streams to train a customized model built on Holoscan and provides real-time colonic polyps identification and classification.
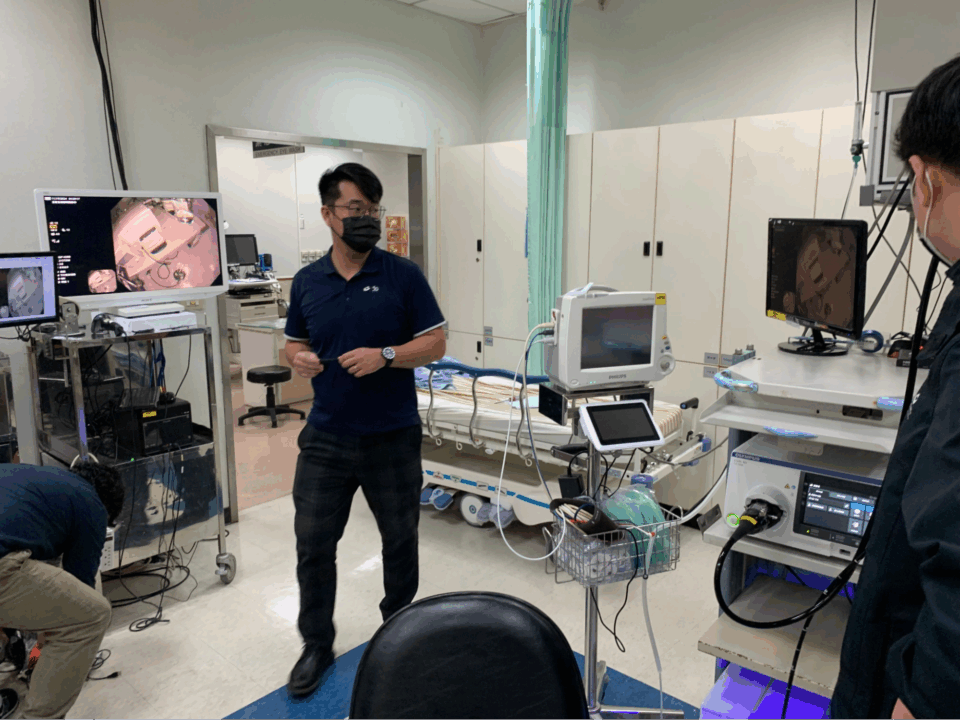
CGMH’s AI infrastructure — comprising NVIDIA accelerated computing, NVIDIA DGX systems, the MONAI framework, NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM open-source library, NVIDIA Dynamo inference framework, and the NVIDIA NeMo and Clara platforms — enables accelerated research and development across the organization.
CGMH serves nearly 50 AI agent models that daily help the hospital analyze medical imaging, improving diagnostic accuracy, throughput and real-time inference at scale. For example, NVIDIA Triton-powered AI sped newborn examination record processing by 10x.
Cathay General Hospital Improves Diagnostics With AI
Cathay General Hospital, a Taipei-based healthcare center that provides hospital management and medical services, has worked with Onyx and software provider aetherAI to develop an AI-assisted colonoscopy system that highlights lesions, detects hard-to-spot polyps and issues alerts to help physicians with diagnoses.
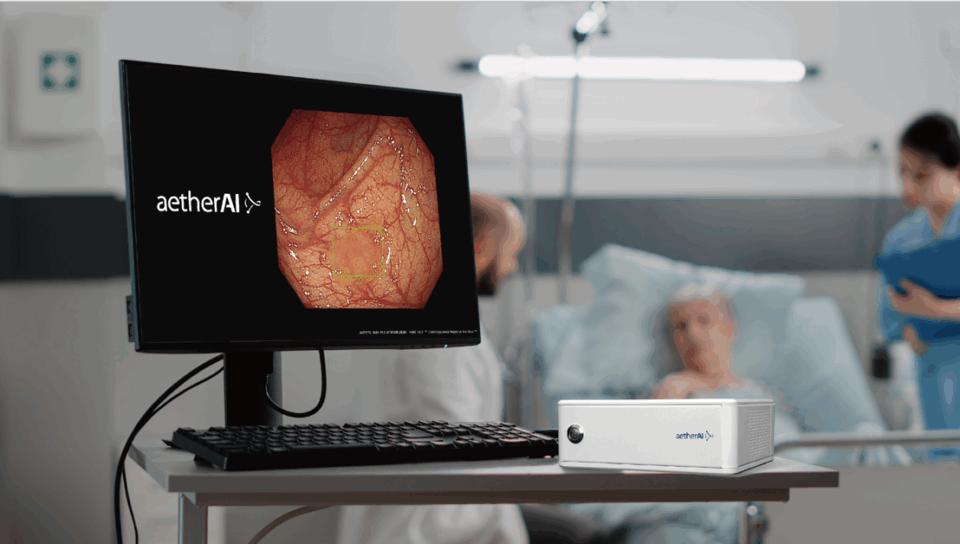
Powered by a compact, plug-and-play AI BOX device — built with the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier module — the AI system is trained on over 400,000 high-quality, physician-annotated images collected from patients with diverse and severe lesions over four years.
Studies have shown the system can achieve up to 95.8% accuracy and sensitivity while improving adenoma detection rates by as much as 30%. These enhancements assist physicians in reducing diagnostic errors and making more informed treatment decisions, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes.
NTUH Detects Liver Tumors, Cardiovascular Risks With AI
In the 100+ years since its founding, NTUH has nurtured countless professionals in medicine and is renowned for its trusted clinical care. The national teaching hospital is now adopting AI imaging to more quickly, accurately diagnose patients.
NTUH’s HeaortaNet model, trained on more than 70,000 axial images from 200 patients, automates CT scan segmentation of the heart, including the aorta and other arteries, in 3D, enabling rapid analysis of risks for cardiovascular disease. The model, which achieves high segmentation accuracy for the pericardium and aorta, significantly reduced data processing time per case from an hour to about 0.4 seconds.
In addition, NTUH collaborated with the Good Liver Foundation and system builder YUAN to develop a diagnostic-assistance system for liver cancer detection during ultrasounds. It taps into an NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX module and a deep learning model trained on more than 5,000 annotated ultrasound images to identify malignant and benign liver tumors in real time.

NVIDIA DeepStream and TensorRT SDKs accelerate the system’s deep learning model, ultimately helping clinicians detect tumors earlier and more reliably. In addition, NTUH is using NVIDIA DGX to train AI models for its system that detects pancreatic cancer from CT scans.
TCVGH Streamlines Multimodal Imaging and Clinical Documentation Workflows With AI
Taichung Veterans General Hospital (TCVGH), a medical center and a teaching hospital administered by the Veterans Affairs Council in Taipei, has partnered with Foxconn to build physical and digital robots to augment staffing, improving clinician productivity and patient experiences.
Foxconn developed an AI system that can analyze medical images and spot signs of breast cancer earlier than traditional methods, using NVIDIA Hopper GPUs, NVIDIA DGX systems and the MONAI framework. By tapping into clinical data and multimodal AI imaging, the system creates 3D virtual breast models, quickly highlighting areas of concern in scans to help radiologists make faster, more confident decisions.
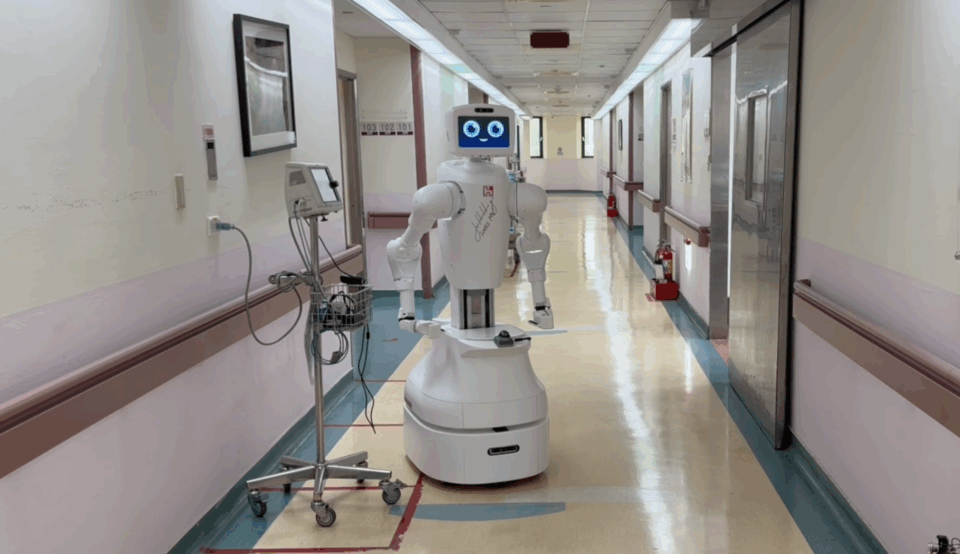
Foxconn is also working with TCVGH to build smart hospital solutions like the AI nursing collaborative robot Nurabot and tapping into NVIDIA Omniverse to create real-time digital twins of hospital environments, including nursing stations, patient wards and corridors. These digital replicas serve as high-fidelity simulations where Jetson-powered service robots can be trained to autonomously deliver medical supplies throughout the hospital, ultimately improving care efficiency.

In addition, TCVGH has developed and deployed its Co-Healer system, which integrates the Taiwanese native large language model TAIDE-LX-7B to streamline clinical documentation processes with agentic AI.
Co-Healer, built on the NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX module, processes and helps summarize medical documents — such as nursing progress notes and health education materials — and supports medical exam preparation by providing students with instant access to nursing guidelines and patient-specific protocols for clinical procedures and diagnostic tests. This helps healthcare workers alleviate burnout while giving patients a clearer understanding of their diagnoses.
Learn more about the latest AI advancements in healthcare at NVIDIA GTC Taipei, running May 21-22 at COMPUTEX.



